三角関数
Contents
三角関数#
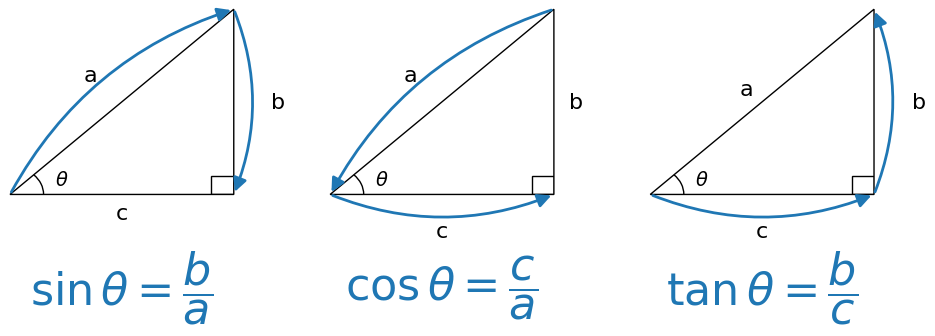
三角形の辺の比による定義#
import numpy as np
import numpy.linalg as LA # 行列計算のため
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as pat # 図形描画のため
def my_triangle(ax, points, arrow, label):
# 三角形
patch = pat.Polygon(xy=points, fill=False, clip_on=False)
ax.add_patch(patch)
# 角マーク
ang = 45
arc = pat.Arc(xy=points[0, :], width=0.3, height=0.3, theta1=0, theta2=ang)
ax.add_patch(arc)
# 角度ラベル
ax.annotate(r'$\theta$', xy=points[0, :], xytext=points[0, :]+np.array([0.2, 0.05]), size=14)
# 直角マーク
rec_size = 0.1
rec = pat.Rectangle(xy=points[1, :]-np.array([rec_size, 0]), width=rec_size, height=rec_size, fill=False)
ax.add_patch(rec)
# 辺ラベル
for p1_num, p2_num, arrow, text in arrows:
# 辺を描くための2点
p1 = points[p1_num, :]
p2 = points[p2_num, :]
# 辺p1p2の中点
p4 = p1+(p2-p1)/2
# 辺Cp1を左に90度回転させた点
p5 = np.array([[0, -1],[1, 0]]) @(p2-p4) + p4
# 辺ラベル
if arrow:
p5 = (p5-p4)/LA.norm(p5-p4)*0.2 + p4
else:
p5 = (p5-p4)/LA.norm(p5-p4)*0.1 + p4
ax.text(*p5, text, size=16,
horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')
# 辺矢印
if arrow:
ax.annotate('', xy=p1, xytext=p2, arrowprops=dict(
arrowstyle=arrow,
linewidth=2, # width
mutation_scale=20, # head size
connectionstyle="arc3,rad=0.2",
color='tab:blue'
), annotation_clip=False)
ax.text(0.5, -0.5, label,
size = 32,
color = 'tab:blue',
horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')
# 枠を消す
ax.axis("off")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10,5))
## sin
points = np.array([
[0, 0],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]
])
arrows = [
[1, 0, None, 'c'],
[2, 1, '<|-', 'b'],
[0, 2, '<|-', 'a']
]
label = r'$\sin \theta = \dfrac{b}{a}$'
my_triangle(ax[0], points, arrows, label)
## cos
points = np.array([
[0, 0],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]
])
arrows = [
[1, 0, '-|>', 'c'],
[2, 1, None, 'b'],
[0, 2, '-|>', 'a']
]
label = r'$\cos \theta = \dfrac{c}{a}$'
my_triangle(ax[1], points, arrows, label)
## tan
points = np.array([
[0, 0],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]
])
arrows = [
[1, 0, '-|>', 'c'],
[2, 1, '-|>', 'b'],
[0, 2, None, 'a']
]
label = r'$\tan \theta = \dfrac{b}{c}$'
my_triangle(ax[2], points, arrows, label)
fig.tight_layout(pad = 3.0)
plt.show()
単位円による定義#
単位円上の点\(P(x,y)\)と\(x\)軸の作る角\(\theta\)を使うと、三角関数は以下のように表せられる。
import numpy as np
import numpy.linalg as LA # 行列計算のため
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as pat # 図形描画のため
radius = 1.0
angle = 30
theta = np.deg2rad(angle)
x = np.cos(theta)*radius
y = np.sin(theta)*radius
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4,4))
# 円
circle = pat.Circle(xy=(0,0), radius=radius, fill=False, color='tab:gray')
ax.add_patch(circle)
# 斜線
ax.plot([0,x], [0,y], color='tab:red')
# 角マーク
size = 0.5
arc = pat.Arc(xy=(0,0), width=size, height=size, theta1=0, theta2=angle)
ax.add_patch(arc)
ax.annotate(r'$\theta$', xy=(0, 0), xytext=(0, 0)+np.array([0.3, 0.05]), size=14)
# 半径 annotation
ax.annotate('', arrowprops=dict(
arrowstyle='-',
connectionstyle="arc3,rad=0.2",
color='tab:blue'
),
xy=(0, 0), xytext=(x, y),
annotation_clip=False)
ax.text(x=x*0.35, y=y*0.75, s=1, size=14)
# 点P annotation
ax.annotate(r'$P(x,y)=(\cos \theta, \sin \theta)$',
size=16,
xy=(x, y), xytext=(1, y),
annotation_clip=False)
# 軸
ax.set_xticks([0])
ax.set_xticks([x, 1], minor=True)
ax.set_xticklabels(['x', 1], minor=True)
ax.set_yticks([0])
ax.set_yticks([y, 1], minor=True)
ax.set_yticklabels(['y', 1], minor=True)
ax.set_xlim(-1.1, 1.1)
ax.set_ylim(-1.1, 1.1)
ax.grid(linewidth=2)
ax.grid(which='minor', linestyle='--')
# 枠を消す
# ax.axis("off")
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(False)
plt.show()
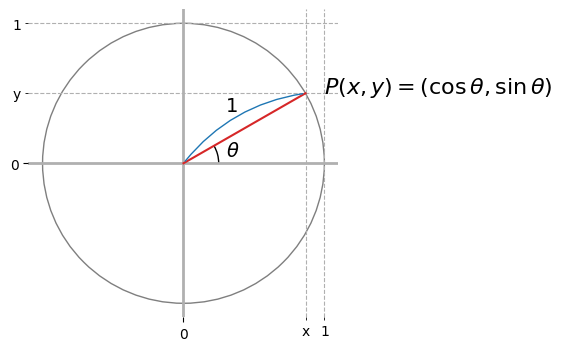
Note
sin(正弦)…正角(注目している角)に対する弦の長さ
cos(余弦)…余角(正角・直角以外の角)に対する弦の長さ
tan(正接)…正角に対する接線の長さ
公式#
導出は、
円の方程式\(x^2+y^2=1\)に\(x=\cos \theta\), \(y=\sin \theta\)を代入
\(\sin^2 \theta+\cos^2 \theta=1\)を\(\cos^2 \theta\)を割る
加法定理#
導出#
正弦定理#
角と正弦と、外接円の半径の関係式
\(\triangle ABC\)において\(AB=c, BC=a, CA=b\)とする。
\(\angle ABC=B, \angle BCA=C, \angle CAB=A\)とする。
\(\triangle ABC\)の外接円の半径を\(R\)とする。
例題:1角2辺の情報から他辺を求める#
a = 4, A = 30º, B = 105º のとき、c の値を求めよ。
– スタディクラブ
正弦定理より、
余弦定理#
隣接する2辺の長さとその間の角、残りの辺の長さの関係式。
\(\triangle ABC\)において\(AB=c, BC=a, CA=b\)とする。
\(\angle ABC=B, \angle BCA=C, \angle CAB=a\)とする。
例題:2辺1角の情報から他辺を求める#
\(a = 3, b = 5, C = 60^{\circ}\) のとき、\(c\) を求めよ。
– スタディクラブ
極限#
微分#
導出#
加法定理\(\sin(x+\alpha)=\sin x \cos \alpha + \cos x \sin \alpha\)を使って
ここで極限の公式 \(\lim_{x\to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1\), \(\lim_{x\to 0}\dfrac{1- \cos x}{x^2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)を使うと、
よって \((\sin x)' = \cos x\)が導かれる。
